Firebase - Part V

Well, today’s idea is to add Firebase to our application. What do I mean? Add one more integrated service to our application. Its only functionality will be to add comments to our application showing something about our task.
First step, let’s go to the Firebase website!
Then let’s go to our console section and create a new project.
After that, it will redirect us to a dashboard:
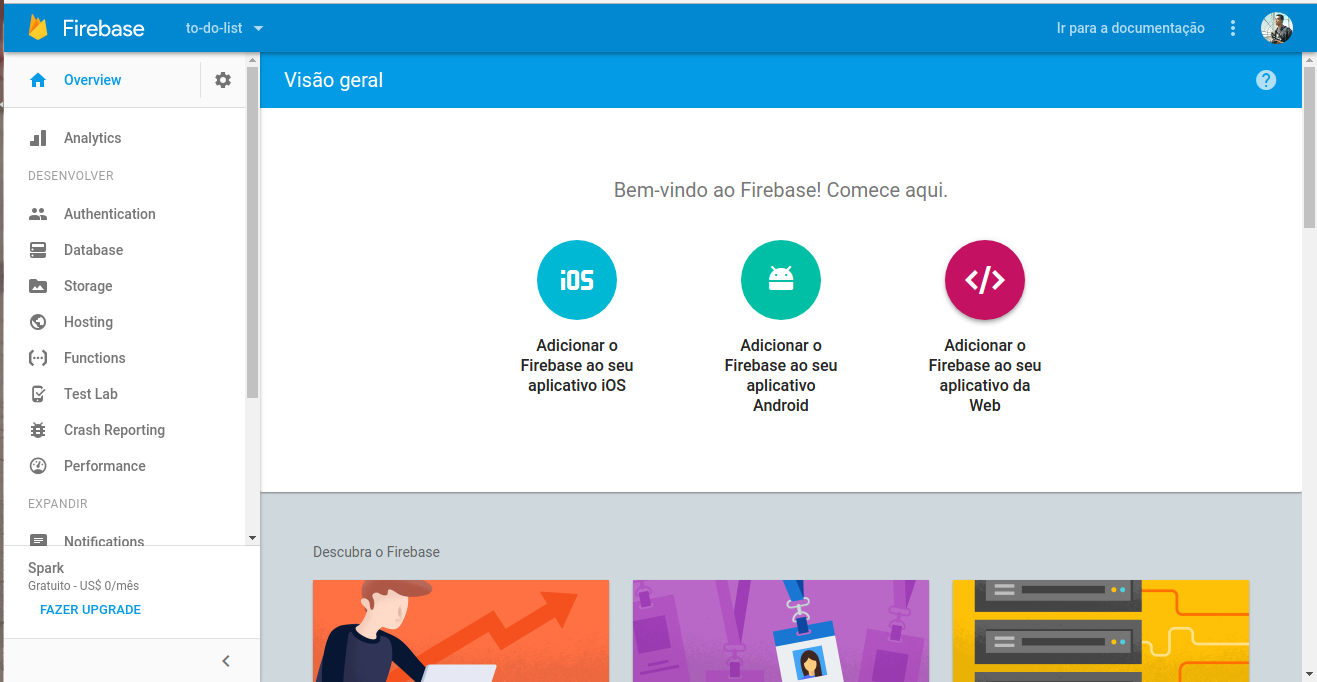
Here are the different applications for which your project can be used. The idea is this: Firebase gives you multiple possibilities to work on your project with both mobile applications for iOS and Android, as well as web. Our case here will be web. Let’s click on the icon to add Firebase to our application.
It will give us the following code:
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/4.1.3/firebase.js"></script>
<script>
// Initialize Firebase
var config = {
apiKey: "your key",
authDomain: "to-do-list-7eabf.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://to-do-list-7eabf.firebaseio.com",
projectId: "to-do-list-7eabf",
storageBucket: "to-do-list-7eabf.appspot.com",
messagingSenderId: "your MessagingSenderId"
};
firebase.initializeApp(config);
</script>
Now we need to disable so we can access our application completely, releasing all roles. Just go to Database, then go to Rules and change the rules object and its keys to true! =]
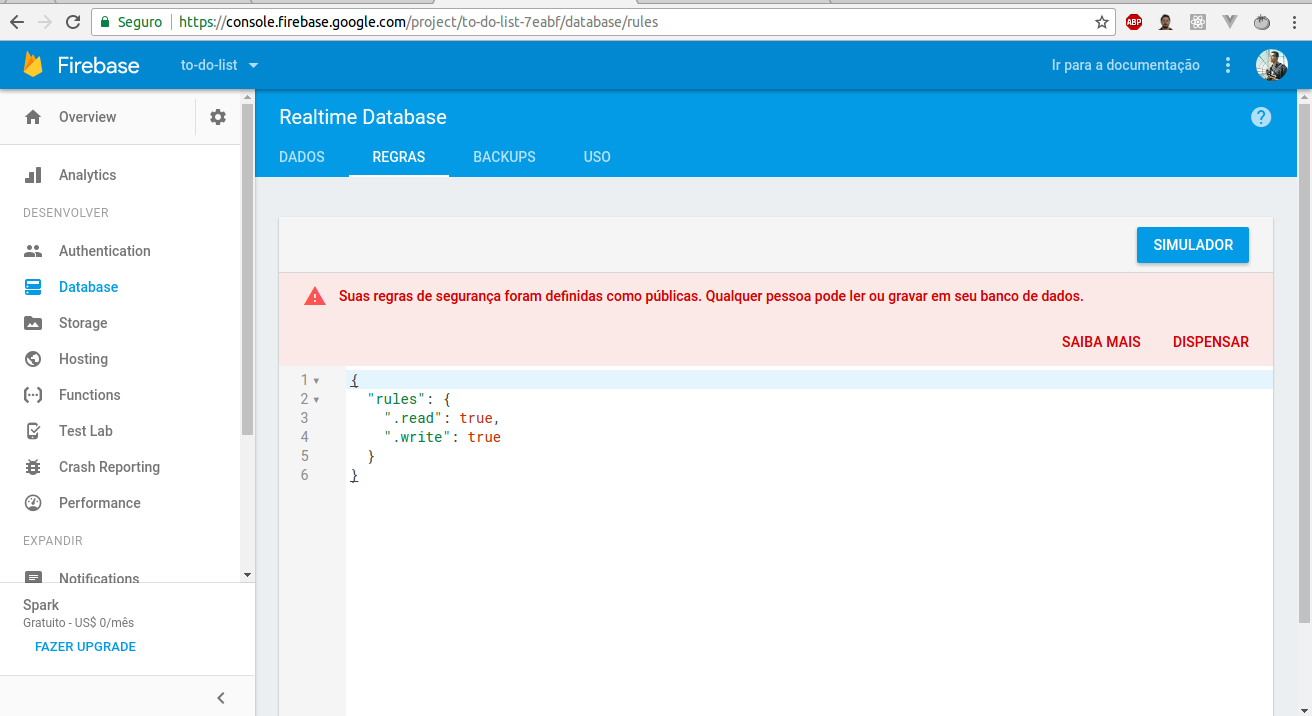
{
"rules":{
".read":true,
".write":true
}
}
PS: This is for demonstration purposes only for educational purposes!
We’ll make some modifications later, but anyway, this is the basics we need. The idea is this: we’ll create a service that will be used in our application to add comments about tasks and be able to remove them. It will be interesting, this part is just a plus. What we need now is to add Firebase and VueFire, a Vue module to communicate with Firebase.
sudo npm i vuefire firebase --save
The first change will be in main.js:
import Vue from 'vue'
/* Vuefire import */
import VueFire from 'vuefire'
import VueResource from 'vue-resource'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import App from './App.vue'
import { routes } from './routes'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(VueFire)
/* Previous code */
Then we need to create our service. It will help us keep communication with Firebase separated from our functions and allow us to call our functions in our Vue template. For this, it’s necessary to create another directory in domain: firebase.
./src/domain/firebase/FirebaseService.js
import Firebase from 'firebase'
const config = {
apiKey: "AIzaSyBY-eZPJrb8Ws_jc1pWCfEhNhF4VzdgC-Q",
authDomain: "to-do-list-7eabf.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://to-do-list-7eabf.firebaseio.com",
projectId: "to-do-list-7eabf",
storageBucket: "to-do-list-7eabf.appspot.com",
messagingSenderId: "893610260697"
};
const app = Firebase.initializeApp(config);
const commentsRef = app.database()
export default commentsRef
I’ll comment on what we did. Here we basically import Firebase - we need it for the configuration part with our application. What we need is to create a way to reference where and how to access our application. We import the module (Firebase), pass the access config, referencing the access key, domain, url, project id, storage - all of this through initializeApp(), which then gives us access to the database() function. Through it, passed to our commentsRef, it allows us to create our objects or delete objects from our database.
Let’s go to our Info.vue, where we’ll make some modifications:
<script>
/* previous imports */
import Comment from '../../domain/comment/Comment'
import commentsRef from '../../domain/firebase/FirebaseService'
export default {
data() {
return {
task: new Task(),
newComments: new Comment(),
id: this.$route.params.id,
msg:'',
title:'Info:'
}
},
firebase() {
return {
comments: commentsRef.ref('comments/' + this.$route.params.id),
}
},
/* previous code */
methods:{
updateTask(){
this.service
.saveTask(this.task)
.then(res => console.log(res))
},
sendComment(){
const justComment = commentsRef.ref(`comments/${this.$route.params.id}`)
justComment.push(this.newComments)
this.newComments = new Comment();
},
removeComment(comment){
const justComment = commentsRef.ref(`comments/${this.$route.params.id}`)
justComment.child(comment['.key']).remove()
}
}
}
</script>
What we did was the following: we imported our service, calling our commentsRef, and we’ll do this: for each comment, it will create a new comment in our database from comments based on our task id, meaning it will only add by id! And then it’s the same as adding values to an array - take the received value and pass it to our array through a push, in Firebase, not in data!, and read the objects of each one. Done. For remove, we just need to indicate the id and we remove the child element to which it was referenced, and that’s it.
If you noticed, we have two more imports. What is this second import? It’s a class. Let’s just add it to our domain/comments/Comment:
export default class Comment {
constructor(comment, owner) {
this.comment = comment
this.owner = owner
}
}
This is just to be able to define what we’ll receive in our comments and what will be passed in our constructor and can be defined with each new comment. It’s very basic, nothing much, just a little something to improve our application.
In our template, let’s make small modifications:
<div class="col-md-4">
<div class="panel panel-info">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h3 class="panel-title">Comments</h3>
</div>
<ul v-for="comment in comments" >
<li class="context">
<span class="person">{{comment.comment}}</span> - <span class="comment">{{comment.owner}}</span>
<i @click="removeComment(comment)" class="glyphicon glyphicon-trash" aria-hidden="true"></i>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<form @submit.prevent="sendComment()" form class="form-horizontal">
<input v-model="newComments.comment" placeholder="Comment..." id="activity" type="text" required class="form-control">
<input v-model="newComments.owner" placeholder="Name..." id="name" type="text" required class="form-control">
<hr>
<button class="btn red">
<i class="fa fa-send"></i>
Post
</button>
</form>
</div>
In our template, we’ll take the comments received in our comments, coming from Firebase, and pass them to our vue-for which will render the objects to be referenced as comment and owner. And in our <i/> we’ll pass our removeComment(comment) function, which receives the comment and removes that specific one by its id. Our other function is just an @submit.prevent - it’s important to add prevent to avoid refreshing the page. Then it receives the values through our model and through our model we send the data to our function from our Firebase service, which in the end updates the data in our Firebase!
Well, that’s it. Later we’ll make some small changes, use linters and some e2e tests, and that’s it. Thank you very much and see you next time! =]